Hey, let’s start your
iObeya journey!
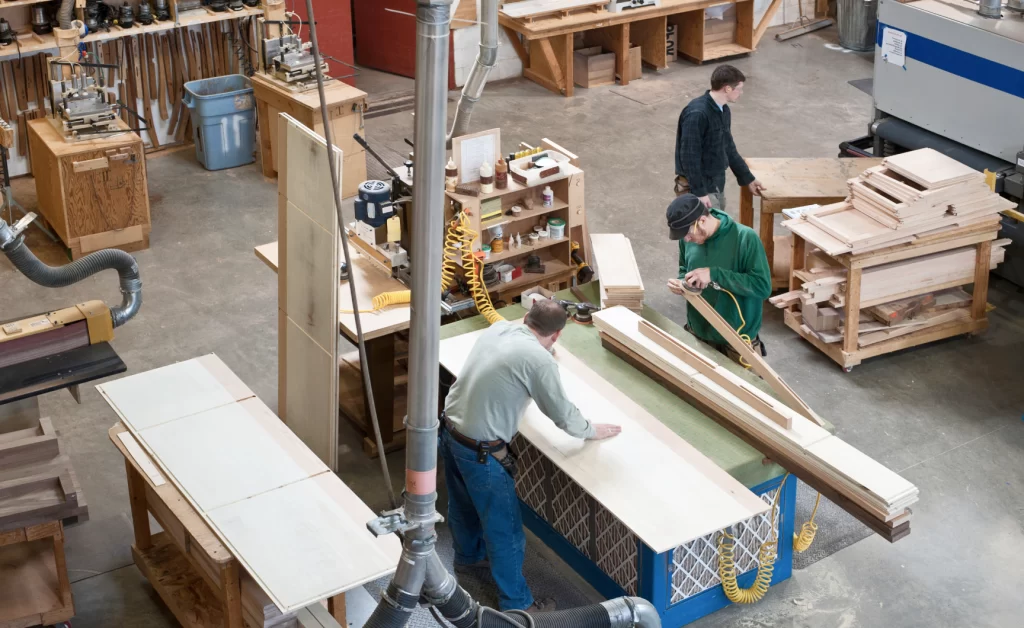
Lean Manufacturing, or Lean Production, is a management approach pioneered by Toyota with the aim of maximizing customer value while minimizing waste. While Lean Manufacturing is a daily practice within large industrial groups, it is equally relevant for SMEs and even small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking improved outputs.
In this article, explore the five fundamental steps to implement Lean Manufacturing within your organization, regardless of its size.
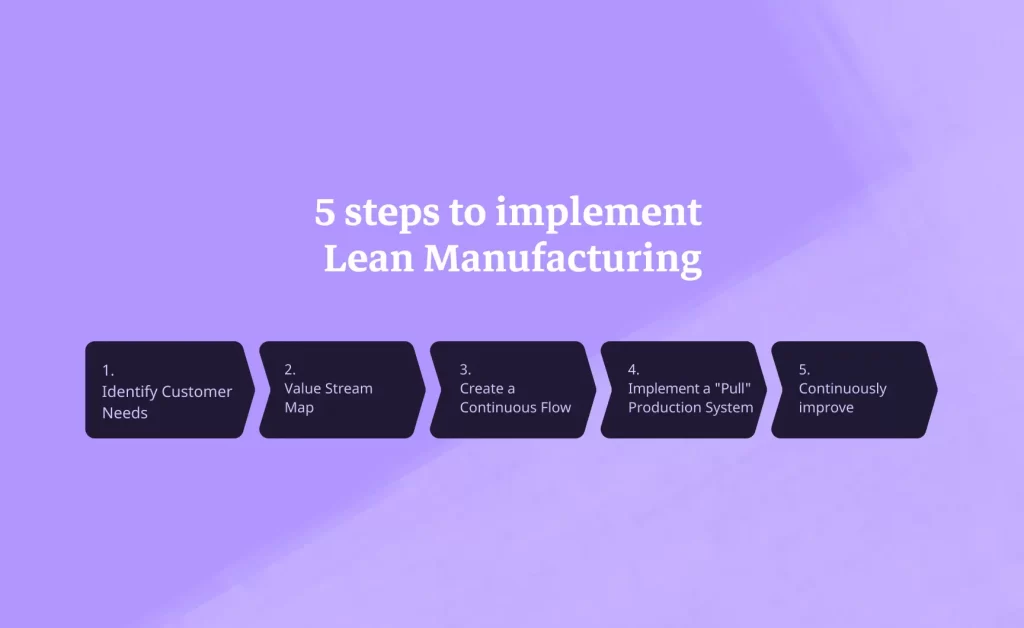
Step 1: Identify Customer Needs
The first step in implementing Lean Manufacturing is to understand the needs and expectations of customers. This involves clearly defining what is considered value from the customer’s perspective. It aims to eliminate anything that does not contribute to perceived value and focuses the team’s efforts in the right direction.
In other words, it’s about aligning customer needs with cultural transformation. To achieve this, organizing workshops with all stakeholders can be valuable to catalyze a cultural shift in favor of Operational Excellence.
Step 2: Value Stream Map
This step involves mapping the entire production process or value stream to identify steps that truly add value and those that generate waste. The goal is to create a comprehensive view of the process, highlighting inefficient areas to eliminate. It is advisable to map not only physical production processes but also initiatives for the digitization of the production workshop to enhance the continuous improvement process.
Step 3: Create a Continuous Flow
After mapping value streams, the goal is to create a continuous and uninterrupted workflow. This often involves the physical reorganization of the work environment to minimize movements, reduce wait times, and optimize production sequences. The aim is to eliminate downtime and ensure a smooth workflow.
For example, concerning safety, implementing a continuous workflow can lead to the creation of a process limiting unnecessary movements and frequent equipment handling, thereby minimizing potentially hazardous situations. Similarly, anomalies can be addressed promptly through the creation of quality control checkpoints at each stage of the workflow, maintaining high-quality standards throughout the production process.
Step 4: Implement a "Pull" Production System
The concept of “pull” production involves producing only what is necessary, when it is needed. This avoids overproduction and reduces unnecessary stock. “Pull” systems are typically demand-driven rather than forecast-driven, allowing better responsiveness to customer needs.
For instance, implementing a “pull” system can be measured and linked to specific operational objectives. This is notably achievable with the SQCDP board , which enables tracking and easily visualizing KPIs related to inventory or production costs.
Step 5: Continuously improve
Continuous improvement lies at the core of Lean Manufacturing. Once the system is in place, the goal is to constantly refine it. This can be achieved by encouraging employee participation in identifying problems and proposing solutions, implementing methods such as Kaizen (continuous improvement), and continually monitoring performance to identify new improvement opportunities.
More concretely, this step involves continuous performance measurement and early detection of issues. For example, incorporating regular Kaizen sessions where various stakeholders are encouraged to identify improvement paths to make continuous improvement an integral part of the work process.
It’s essential to note that the implementation of Lean Manufacturing is not a one-time process but rather a continuous effort to create a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. To facilitate the implementation of Lean Manufacturing within your organization, opting for a solution compliant with OpEx practices, easy to use, customizable, and capable of integrating data is preferable. The iObeya Lean Agile platform can meet these requirements as it allows visualizing execution plans, flows, key metrics, and facilitates problem resolution.